
Updating Estate Planning After a Dementia Diagnosis
Planning early after a dementia diagnosis ensures that your medical and personal wishes are documented, which can ease future stress and maintain control over decisions as the disease progresses.

Planning early after a dementia diagnosis ensures that your medical and personal wishes are documented, which can ease future stress and maintain control over decisions as the disease progresses.
With more Americans pursuing early testing and care planning, Alzheimer’s disease is no longer viewed only as a crisis, but as a condition to prepare for thoughtfully and strategically.

A head start on estate planning can help you prepare for risks, like dementia. By documenting your legal and financial wishes early, you can safeguard your wishes and provide clarity to loved ones.

Understanding the differences between Alzheimer’s and other types of dementia is crucial for early diagnosis and effective planning.
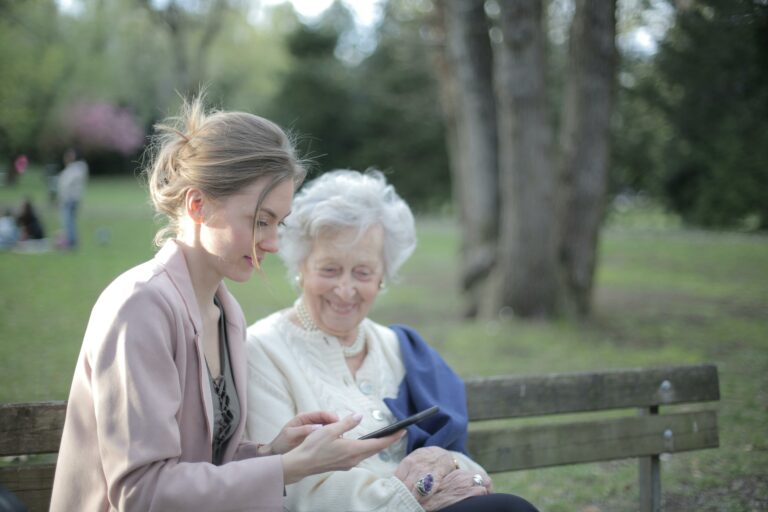

As family members and caregivers notice signs of cognitive decline in loved ones, it is essential to take proactive steps to safeguard assets. Seeking guidance from an elder law attorney to navigate complex planning issues as well as guard against financial exploitation reduces vulnerability to fraud.
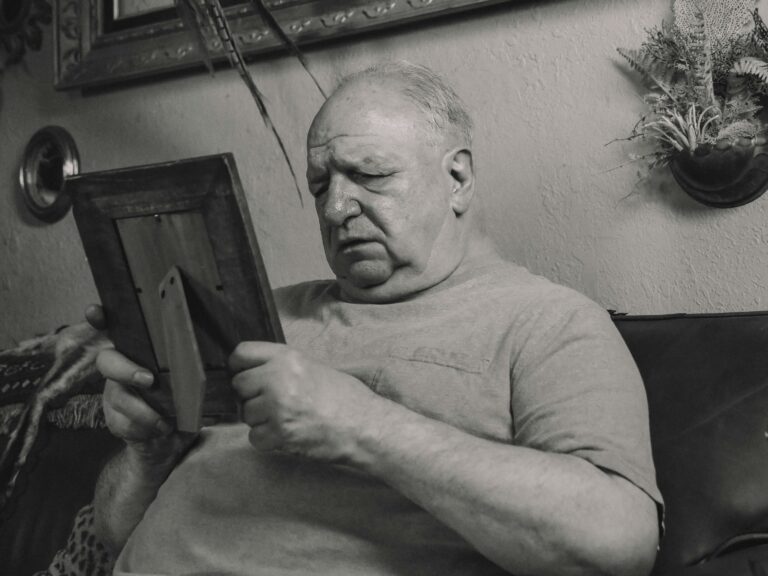

I have been diagnosed with brain damage and dementia. Word to the younger folks: I woke up last year and suddenly could not spell or write legibly. No warning. No symptoms.

Scams are everywhere, and older people are prime targets. It’s critical to be vigilant, safeguard personal info, get paperwork in order and more.

Many older people are one medical emergency away from a court-appointed guardian taking control of their lives.
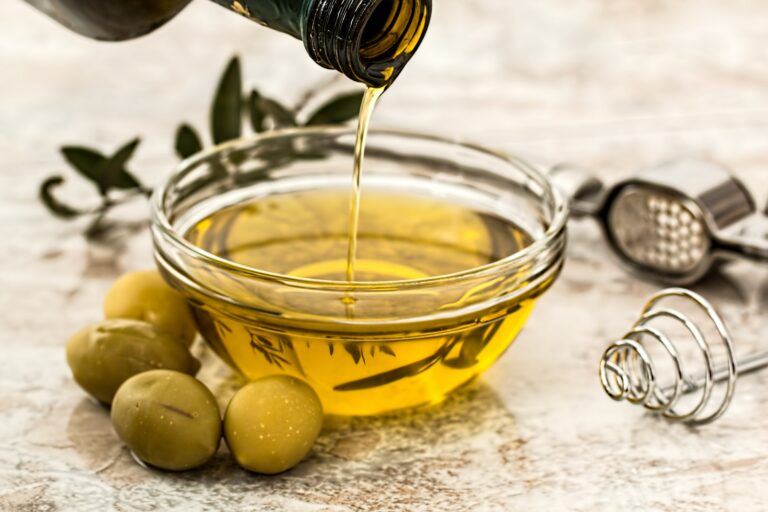

Adding more oil to your cooking may seem of little consequence, but new research shows that consuming more olive oil in your diet could lower your risk of dying from dementia and boost brain health.

At some point, most older people will need help getting through the day. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, someone turning 65 today has a 70% chance of eventually requiring assistance with basic living activities, such as bathing, dressing and using the toilet.