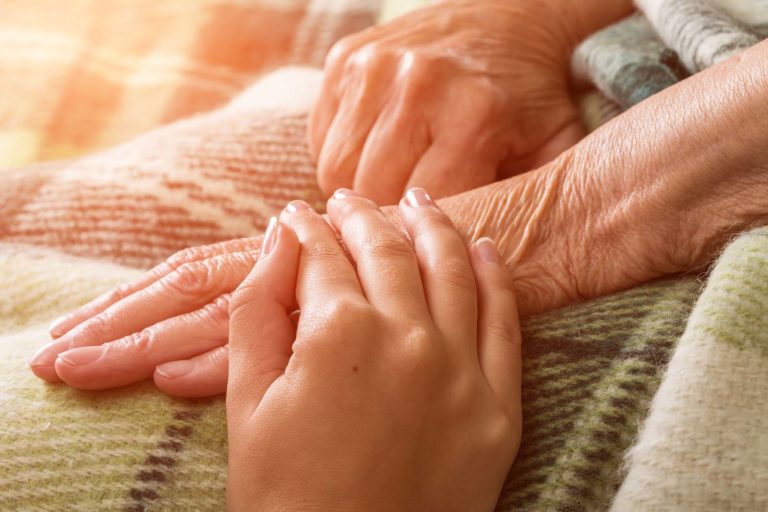

Estate Planning When a Loved One Needs Hospice Care
When someone you love enters hospice, your world can narrow quickly. You are trying to be present, to help them feel safe, and to make

When someone you love enters hospice, your world can narrow quickly. You are trying to be present, to help them feel safe, and to make

Living alone in later years can feel peaceful. However, practical and legal preparation is essential to maintain independence and safety over time.

Unchecked hypertension quietly damages arteries and increases the risk of stroke, especially in older adults who may not notice symptoms until it’s too late.

Estate planning for family members who are older or have disabilities extends far beyond financial considerations.

Planning early after a dementia diagnosis ensures that your medical and personal wishes are documented, which can ease future stress and maintain control over decisions as the disease progresses.

Are you worried that your dad might fall for his caregiver and leave the family farm to her in his will?

The sandwich generation—adults caring for both aging parents and dependent children—must juggle emotional, financial and legal responsibilities all at once.
With more Americans pursuing early testing and care planning, Alzheimer’s disease is no longer viewed only as a crisis, but as a condition to prepare for thoughtfully and strategically.

Older Americans Month reminds us that aging is not a decline but a continuation of growth, contribution and vitality in every stage of life.

Understanding Social Security rules and benefits is essential for financial security in retirement. An elder law attorney can help you make informed decisions.