Why Is Communication Important in Estate Planning?
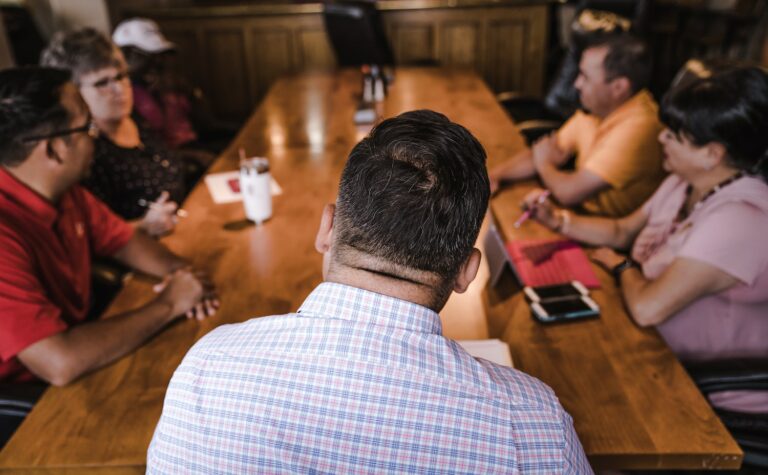
Successful transition of wealth from generation to generation is best accomplished when family members have a shared understanding of the overall use of the family wealth. While the initial wealth creators have final say about how their assets are distributed, awareness and agreement on the part of the receiving family members regarding how the wealth is used can help preserve assets as they move to the next generation.
Forbes’ recent article entitled “Communication Can Be The Key To Creating Harmony In Multi-Generational Estate Planning” says that coming to an agreement can sometimes be difficult, especially if family members bring their own perspectives and values to the estate planning process. However, good communication can help head off potential multi-generational conflicts before they happen.
One of the most significant challenges in achieving multi-generational wealth preservation is that each individual and generation has a different outlook on wealth. Today’s families could include four or even five generations. This big gap in ages could mean differing perspectives on many topics, including:
- Personal values. Family members may have different belief systems and values, including how they view work, social and political systems, relationships, and other topics.
- Investing priorities. Some generations may give greater importance to socially conscious investing than others. This could create a conflict when it comes to how and where to invest.
- Shifting economic environments. Older generations who have lived through various economic scenarios may have very different perspectives than younger generations, particularly those just coming of age in a time of high inflation and a slowing economy.
- Communication. Not every generation or family member is comfortable talking openly about money, especially when it comes to sharing how much is involved and how to spend it.
- View of the role of a financial advisor. Some family members may see a financial advisor as a trusted partner, and others may be more skeptical.
While these differences can create challenges in the estate planning process, you can resolve them and reach an agreement about how to best manage the family’s wealth. Begin with a plan designed for the long-term, spanning current and future generations that’s flexible to meet the family’s changing needs and shifting economic environments.
Reference: Forbes (April 18, 2022) “Communication Can Be The Key To Creating Harmony In Multi-Generational Estate Planning”