How to Protect Loved Ones from Elder Abuse
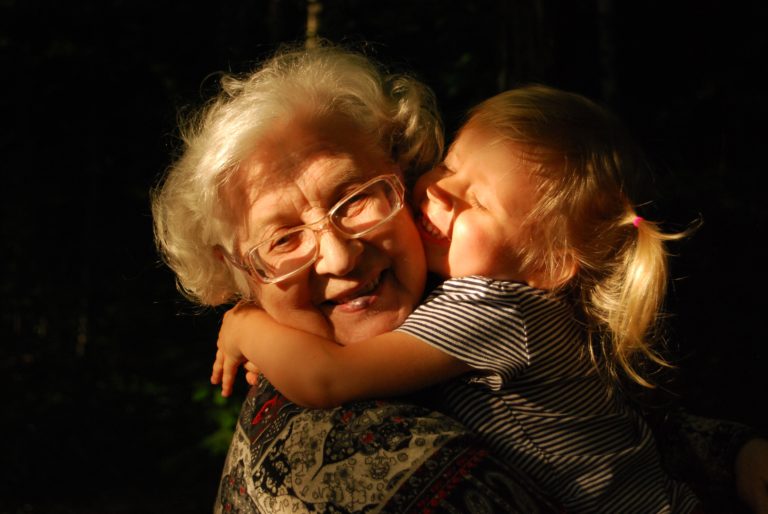
Predators had an open season on the elderly during the pandemic, as isolation necessitated by COVID severely limited family member’s ability to visit in person. In some instances, caregivers themselves were the predators, and manipulation on important legal documents, including durable power of attorney, trusts, wills and ownership of homes has occurred. All this was reported the article “Warning: Isolation Of Your Aging Parent May Be A Red Flag” from Forbes. The enforced isolation has created worrisome situations for all concerned.
If you haven’t seen your parents or grandparents for a year or more, and are all fully vaccinated, one expert strongly encourages visitation, as soon as is possible. Use the visit to review all of their legal matters and talk about how to increase engagement and end the isolation.
Consider the following a checklist of what needs to be done at that first visit:
Look for any signs that anyone who had access to loved ones may have taken advantage of their isolation during the past year. Don’t assume the best behavior of everyone around them. It’s not how we like to think, but caution needs to be exercised in this situation.
Check on their will and trusts. The pandemic has reminded everyone that life is fragile, and it’s important to go over legal documents or, if they don’t exist, create them. Find out if anyone has pressured family members to change legal documents—if they have been changed in the last year and you weren’t told about it, find out what happened.
If aging parents do not have a will or trusts, or these documents were altered in your absence, speak with an estate planning attorney who can create a new estate plan. Make sure all copies of older wills are destroyed. At the same time, this would be a good time to have their powers of attorney, healthcare proxy and living wills updated.
If your parent or grandparent lives on their own, find out if they are now in need of any caregiving. A year is a long time, and elderly people who started out fine during the epidemic may have had changes in their health or ability to live independently. Go see for yourself how they are managing. Is the house clean? Are the stairs too steep to be managed?
Not everyone will be able to return to “normal” without some help. Senior centers, gyms and recreational facilities have been shut down for a long time. They may need some help getting back into a routine of socializing and exercising.
The end of enforced isolation can also mean the end of an easy cover for anyone who was using isolation as a protection for financial elder abuse or any other type of abuse.
Isolation itself is a form of abuse, including not allowing others to visit in person or speak with a parent alone. You can overcome this by being engaged with family members on a regular basis, by phone, video visits or, if you are able to, more frequent in person visits.
Reference: Forbes (April 23, 2021) “Warning: Isolation Of Your Aging Parent May Be A Red Flag”